Table of Content
TL;DR
Introduction
The Perfect Storm
The AI Solution
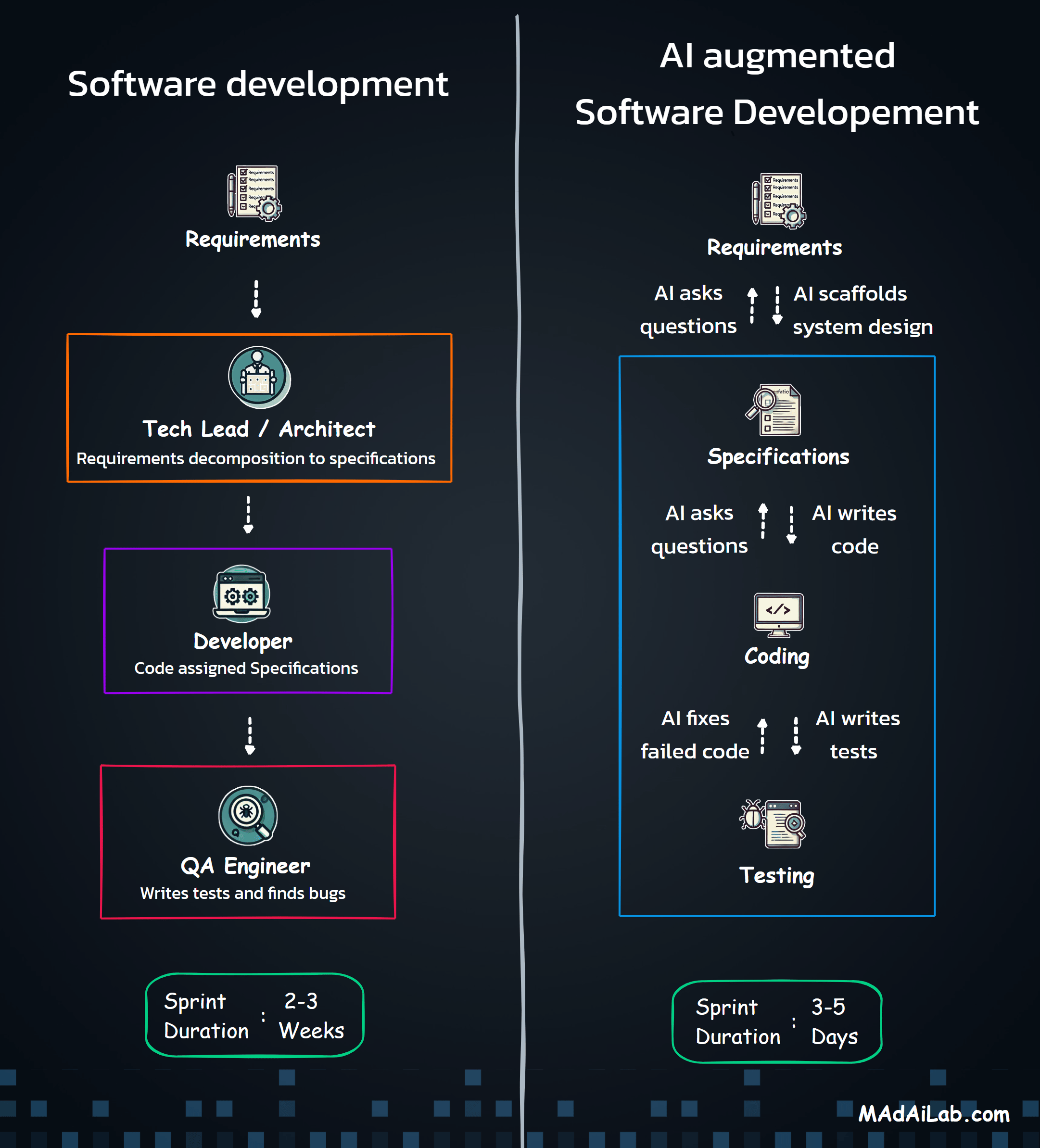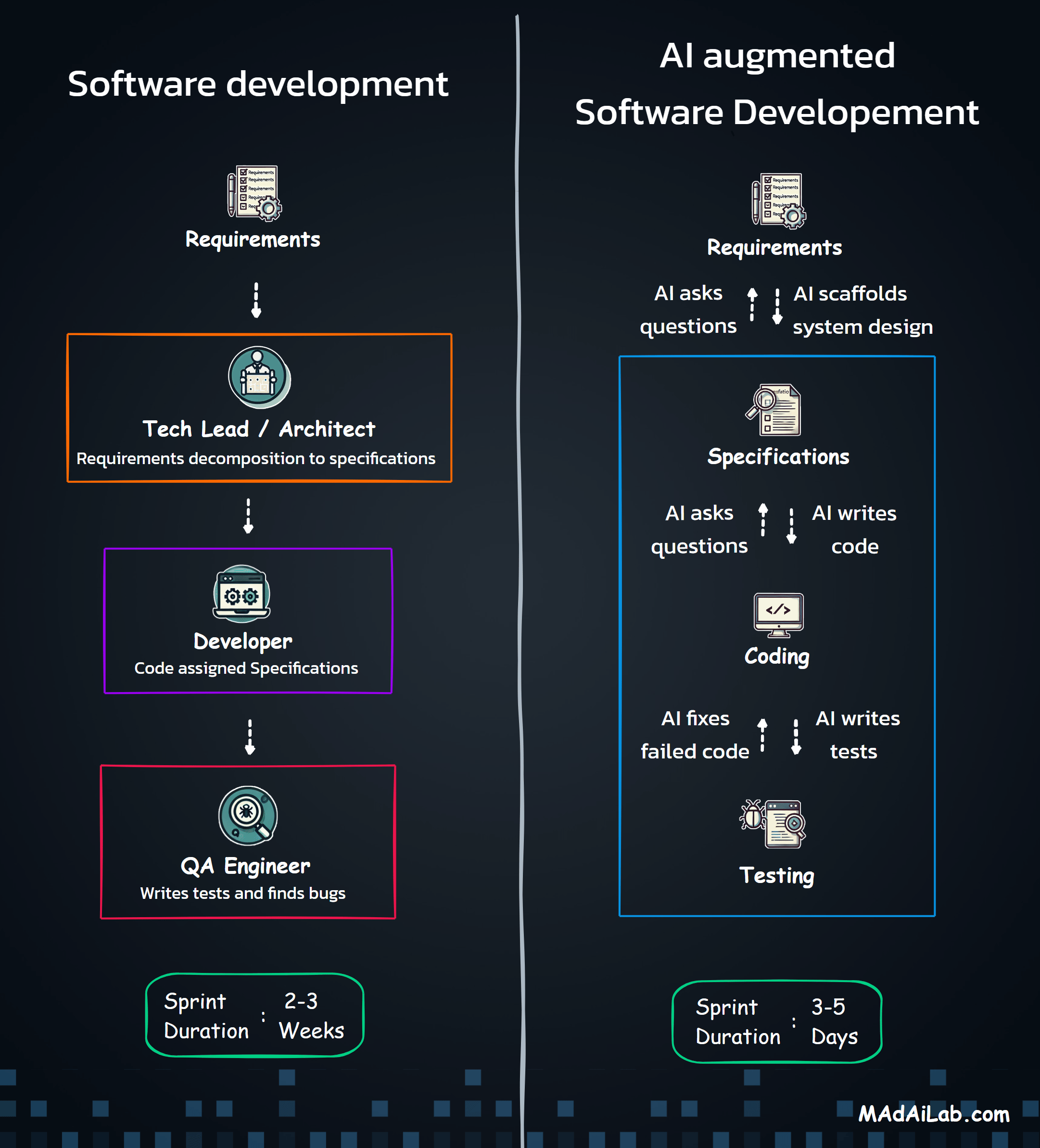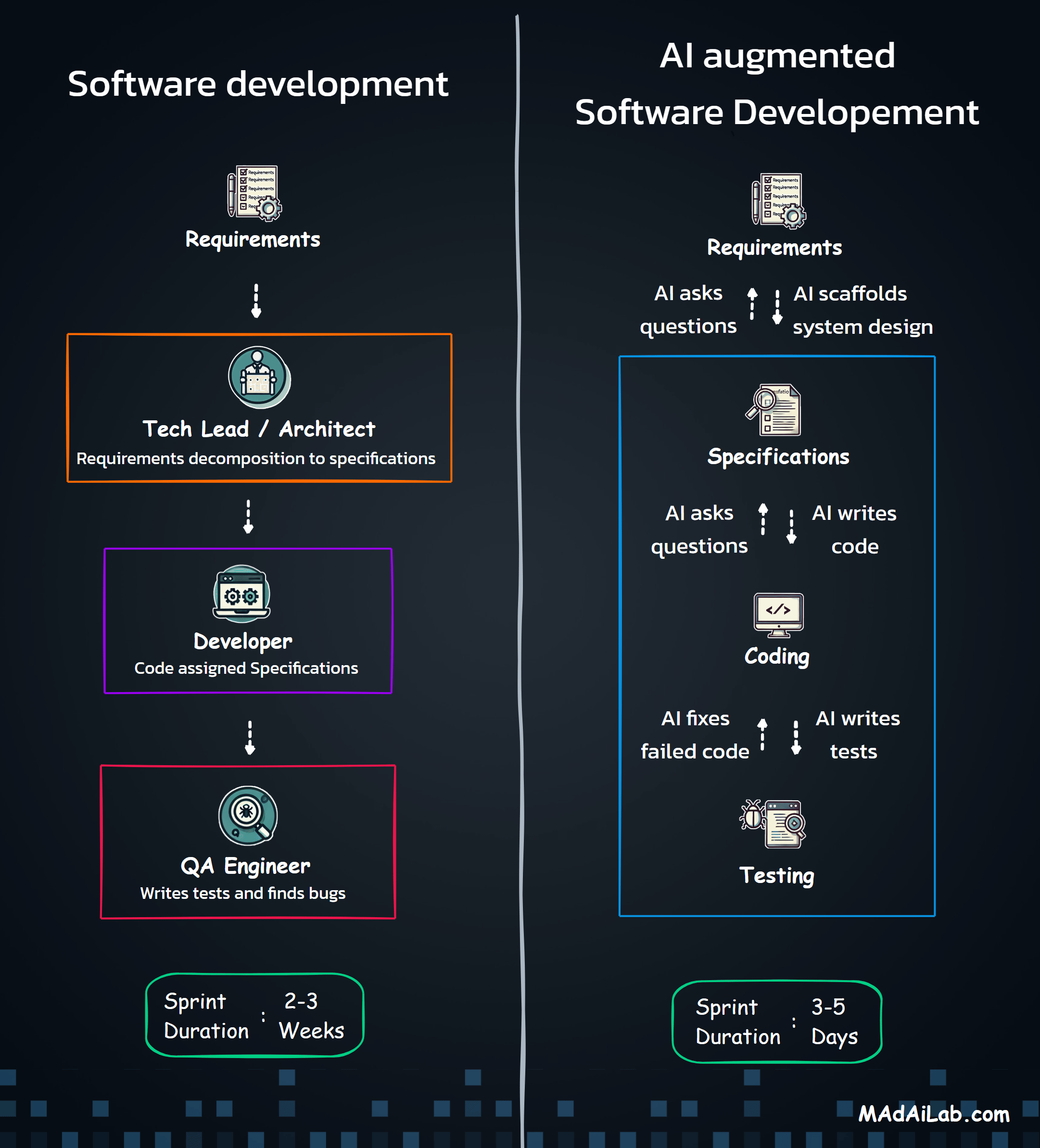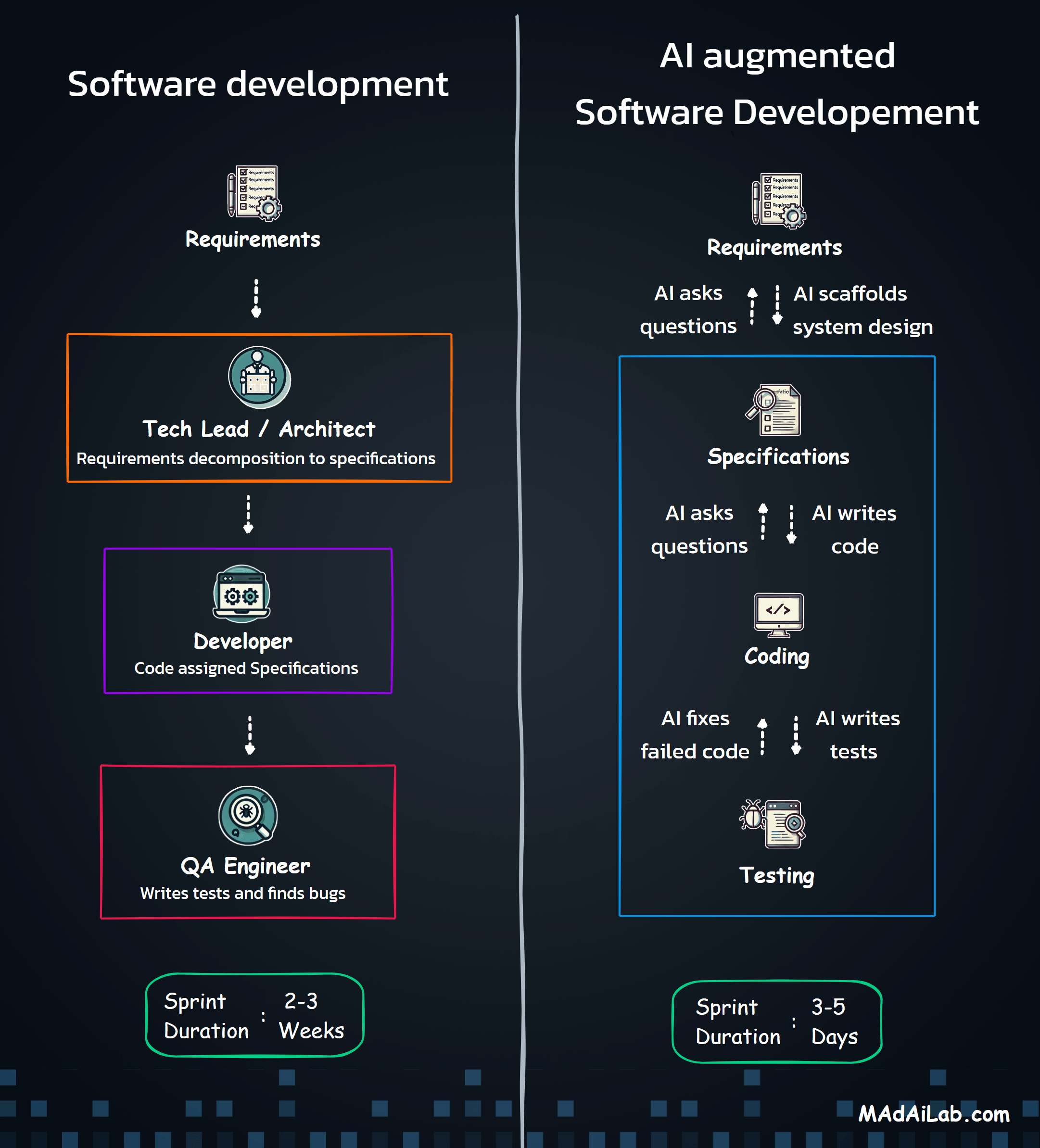
Why Orchestration?
The Five Processing Pipelines
Request Flow: An Email's Journey
Why Multiple Agents?
The Three Core Agents
Agent 1: The Compliance Expert
Agent 2: The Pattern Detective
Agent 3: The Strategic Communicator
Agent Coordination Flow
The Hallucination Problem
Rule Retrieval Architecture
Rule Evaluation Process
The Forest and Trees
Automated Clustering
Trend Detection
Why Vector Search Matters
Use Cases
Search Process
The Speed Imperative
Multi-Channel Alerting
Live Dashboard Updates
The Quality Paradox
Email Generation Strategy
Transaction Generation
Database Foundation
Maintenance Operations
Performance Monitoring
Authentication
Authorization
Comprehensive Audit Logging
Centralized Error Processing
Intelligent Retry Logic
Core Patterns Recap
Conclusion: The Future of Compliance is Intelligent
Key Principles
Bio
Building a Multi-Agent AI Compliance (eg SOX) System: Master Orchestrator Architecture with RAG, Vector Search, and Real-Time Monitoring
A production-grade architecture that analyzes 100% of organizational communications using specialized AI agents, retrieval-augmented generation for rule enforcement, and thematic clustering to transform reactive auditing into proactive risk management
TL;DR
This guide presents a production-grade architecture for AI-powered compliance monitoring that analyzes 100% of communications in real-time. Key components:
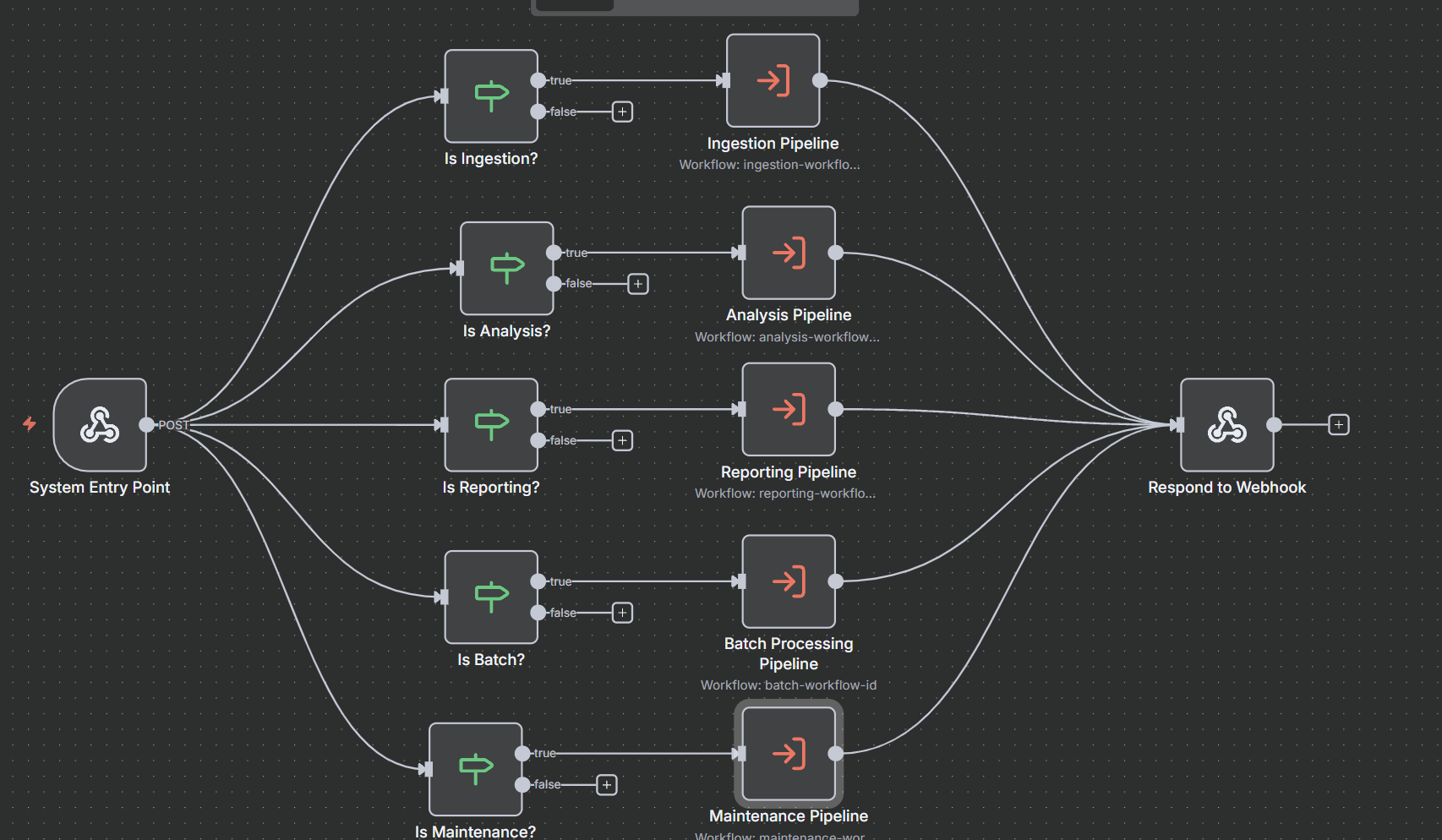
- Master Orchestrator coordinates five specialized processing pipelines (ingestion, analysis, reporting, batch, maintenance)
- Three specialized AI agents (Compliance Expert, Pattern Detective, Strategic Communicator) work in coordination for comprehensive analysis
- RAG-powered rule engine prevents AI hallucination by grounding responses in actual compliance policies via vector search
- Thematic clustering transforms individual violations into systemic intelligence revealing organizational patterns
- Real-time multi-channel alerting enables immediate response to critical violations
- Comprehensive error handling, security, and audit trails ensure production readiness
The architecture is technology-agnostic, applicable across workflow automation tools, traditional frameworks, or serverless platforms. It transforms compliance from reactive sampling (1-5% coverage) to proactive monitoring (100% coverage) with real-time detection.
Introduction
A single compliance violation can cost millions in fines and permanent reputational damage. Yet traditional audit approaches examine only 1-5% of organizational communications. This guide presents a production-grade architecture for AI-powered compliance monitoring that analyzes 100% of communications in real-time, transforming compliance from reactive auditing to proactive risk management
While we reference specific technologies as examples, the architectural patterns apply across platforms—workflow automation tools, traditional frameworks, or cloud-native architectures.
1. The Problem: Why Traditional Compliance Fails
The Perfect Storm
Modern organizations face an impossible challenge:
- Regulatory Complexity: Simultaneous compliance with SOX, GDPR, FCPA, HIPAA, and industry-specific regulations across multiple jurisdictions
- Data Deluge: A 1,000-person company generates 50,000+ daily emails, 10,000+ weekly transactions
- The 1% Problem: Manual audits sample only 1-5% of data, leaving 95% unexamined
- Detection Gap: Issues go undetected for months or years, compounding damage exponentially
The AI Solution
Intelligent automation transforms the game:
- Analyze 100% of communications in real-time
- Detect subtle patterns across millions of data points
- Provide immediate alerts for high-risk activities
- Learn and adapt as regulations evolve
- Scale infinitely without proportional headcount increases
2. Core Architecture: The Master Orchestrator Pattern
Why Orchestration?
Building compliance isn't one process—it's coordinating dozens of specialized operations. The Master Orchestrator acts as the system's nervous system, receiving requests, routing to appropriate pipelines, coordinating sub-processes, and managing state across complex operations.
Key Principle: Like a conductor coordinating musicians, the orchestrator ensures specialized processes work in harmony rather than chaos.
The Five Processing Pipelines
1. Ingestion Pipeline - Data onboarding and normalization
- Connects to email servers, document repositories, file uploads
- Parses content, extracts metadata, removes duplicates
- Structures data for downstream analysis
2. Analysis Pipeline - AI-powered compliance analysis (the intelligence core)
- Flows through initialization → multi-agent coordination → risk assessment → alert generation
- Raw communications enter; actionable insights with evidence emerge
3. Reporting Pipeline - Strategic intelligence
- Transforms individual findings into strategic insights
- Thematic clustering, trend detection, stakeholder-specific reports
- Produces executive summaries, board reports, audit documentation
4. Batch Processing Pipeline - Historical analysis and bulk operations
- Efficiently analyzes large datasets (years of archived communications)
- Upload → parsing → iterative analysis → result aggregation
5. Maintenance Pipeline - System health and optimization
- Validates permissions, routes administrative tasks
- Database optimization, performance monitoring, data archival
- Keeps system running without manual intervention
Request Flow: An Email's Journey
- Entry → New email triggers orchestration endpoint
- Classification → Orchestrator determines request type
- Routing → Selects appropriate processing pipeline
- State Initialization → Tracks execution across steps
- Sequential Coordination → Executes sub-processes in order
- Conditional Routing → Makes decisions based on intermediate results
- Aggregation → Merges outputs from all processes
- Error Handling → Catches failures, implements recovery
- Audit Trail → Logs every step for compliance documentation
- Response → Returns structured results with violations, recommendations, evidence
Critical Pattern: The orchestrator maintains context, implements graceful degradation, tracks metrics, and enforces consistent error handling across all pipelines.
3. Multi-Agent Intelligence: Specialized AI for Specialized Tasks
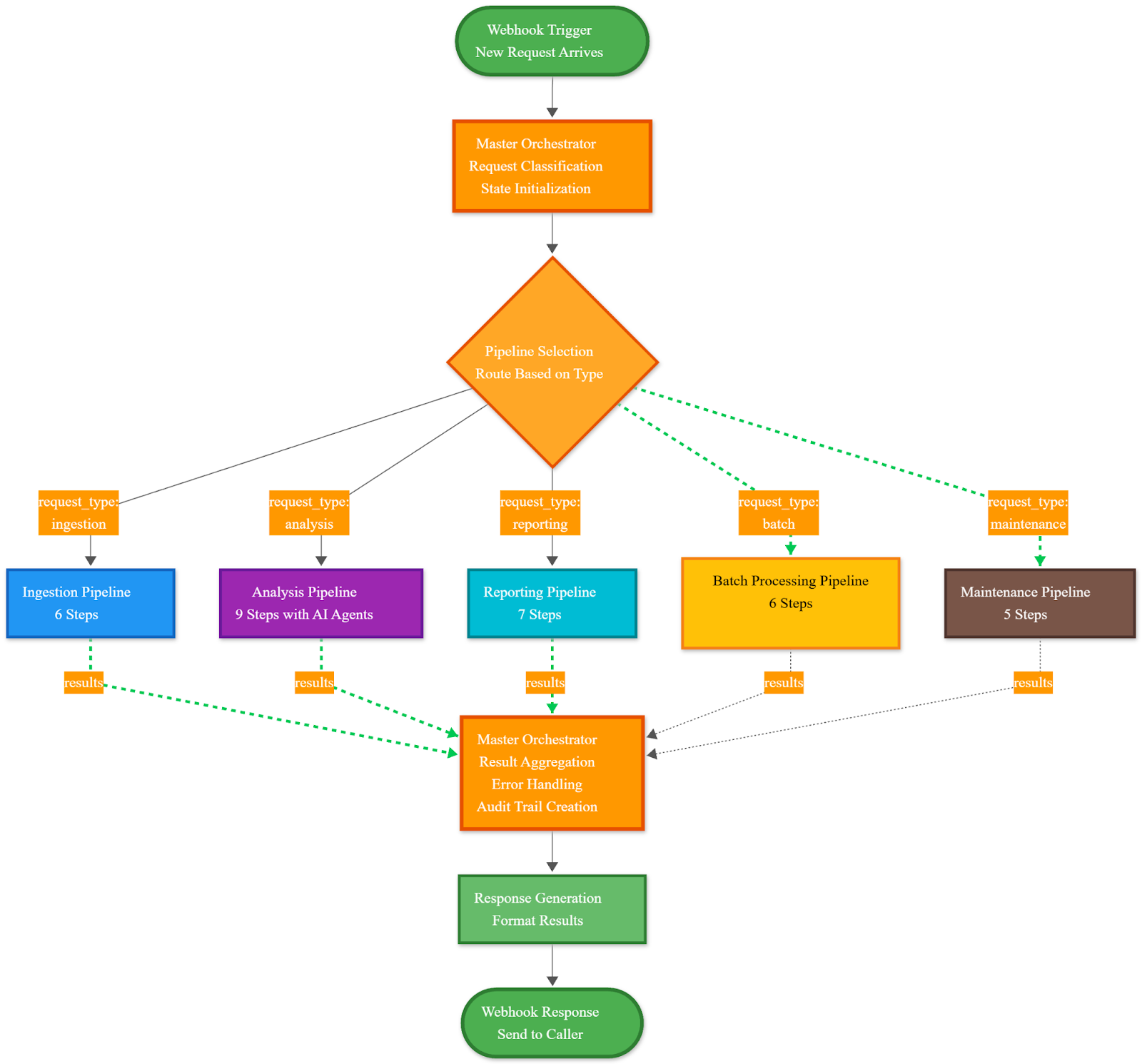
Why Multiple Agents?
A single AI model cannot excel at rule-based compliance checking, statistical anomaly detection, AND strategic reporting simultaneously. The multi-agent approach leverages specialized models for specialized tasks.
Pattern: Agent coordination via state machine workflow that initializes shared context, routes documents through specialized agents, manages conditional logic, aggregates findings, and calculates composite risk scores
The Three Core Agents
Agent 1: The Compliance Expert
Specialty: Rule-based compliance and policy interpretation
Performs deep semantic analysis, classifying content into risk categories (compliant, potential violation, edge case, false positive trap). Doesn't just find keywords—understands context, intent, and implications.
Example: "Let's discuss this offline" in a product launch email is benign. The same phrase in financial reporting emails before quarter-end? Red flag for potential earnings manipulation.
Core Capabilities:
- Semantic understanding using LLMs
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) for rule application
- Context-aware classification with confidence scoring
- Evidence extraction and citation
Detection Categories: Gift acceptance violations, insider trading indicators, conflicts of interest, data privacy breaches, harassment, financial reporting irregularities.
Agent 2: The Pattern Detective
Specialty: Statistical and behavioral anomaly detection
Combines quantitative and qualitative approaches to identify unusual patterns.
Statistical Component:
- Outlier detection (Z-scores, IQR)
- Frequency anomalies (unusual volumes)
- Timing patterns (after-hours, holiday activities)
- Threshold manipulation detection (just-below-limit patterns)
Semantic Component:
- Language pattern recognition (urgency, secrecy, coercion)
- Sentiment analysis for inappropriate tone
- Communication style deviation
- Relationship graph analysis
Example: Employee receives three $249 gifts from same vendor (limit is $250). Statistical engine flags three near-threshold transactions in short timeframe. Semantic engine notices "just a small token" and "no need to report this" in emails. Together: clear threshold avoidance pattern.
Agent 3: The Strategic Communicator
Specialty: Synthesis, prioritization, and actionable reporting
Transforms technical findings into strategic intelligence tailored for different stakeholders.
Core Functions:
- Risk score calculation using weighted ensemble methods
- Executive summaries in accessible language
- Detailed violation documentation with evidence chains
- Remediation recommendations
- Multi-format output (dashboard, PDF, email, API)
Stakeholder Adaptation:
- CFO: Financial risk exposure and regulatory implications
- Legal: Evidence trails and procedural compliance
- Board: High-level risk trends and governance effectiveness
- Compliance Officers: Actionable items with clear next steps
Agent Coordination Flow
Initialization → Load document, organizational context, user profile, compliance rules, baseline patterns
Sequential Processing → Agent 1 establishes baseline → Results inform Agent 2 focus → Agent 2 findings influence Agent 3 prioritization
Conditional Routing → High-risk findings trigger deeper analysis → Edge cases activate human review → Low-confidence assessments trigger additional agents
Error Recovery → Fallback to simpler analysis if advanced methods fail → Partial results if some agents error → Retry logic with exponential backoff
4. The RAG-Powered Compliance Rule Engine
The Hallucination Problem
LLMs hallucinate—confidently stating plausible but fabricated regulations. You cannot have an AI inventing compliance rules.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) solves this: Instead of asking the AI to recall regulations, provide the exact, current text of relevant rules for every analysis.
Core Principle: Don't ask "What are the rules about gifts?" Ask "Here are the exact gift acceptance rules [provides text]. Does this email violate them?"
Rule Retrieval Architecture
Indexing (One-Time Setup):
- Gather all compliance rules, policies, procedures
- Break long documents into semantic chunks
- Convert text to high-dimensional vectors (embeddings)
- Store embeddings in vector database
- Maintain references between vectors and source documents
Retrieval (Per Analysis):
- Extract key compliance concepts from document
- Convert query to vector
- Find 5-10 most similar rule vectors
- Rank by relevance score and priority
- Retrieve full rule text with metadata
- Provide rules to analysis agent as context
Example: Analyzing email about conference sponsorship retrieves: gift acceptance policy, FCPA promotional expense guidance, industry regulations, recent clarifying memos, historical examples, threshold tables, approval workflows.
Rule Evaluation Process
Construct sophisticated prompts with role definition, retrieved rules, document to analyze, violation/compliant examples, organizational context, analysis requirements, and structured output format.
Workflow: Construct prompt → Send to LLM → Parse structured response → Extract violations, confidence, evidence → Validate logical consistency → Return to Compliance Expert agent
Quality Assurance: Cross-reference across rules, verify evidence citations, flag low-confidence assessments, track false positives, continuous improvement through feedback.
5. Thematic Analysis: From Incidents to Systemic Intelligence
The Forest and Trees
Individual violations are data points. Real value comes from systemic patterns: Is Sales consistently pushing ethical boundaries at quarter-end? Are conflicts of interest more common in certain geographies? Are gift violations increasing month-over-month?
Key Insight: One gift violation is a training issue. A pattern of gift violations in Sales during Q4 every year is a systemic cultural problem requiring executive attention.
Automated Clustering
Data Preparation: Fetch vector representations → Combine textual embeddings with metadata → Apply dimensionality reduction → Normalize features
Clustering Process: Select algorithm (K-means, DBSCAN, hierarchical) → Determine optimal cluster count → Assign violations → Validate meaningfulness
Theme Extraction: Generate descriptive names → Identify representative examples → Analyze unique characteristics → Calculate trends over time
Example Discovered Themes:
- "Vendor Gift Threshold Gaming" (15 incidents, gifts just below reporting limits)
- "Personal Account Data Exfiltration" (23 incidents, sensitive data to personal emails)
- "After-Hours Confidential Communications" (12 incidents, financial info outside business hours)
Trend Detection
Data Collection: Query violations for 30-90 days → Group by dimensions (time, department, type) → Calculate metrics → Establish historical baselines
Analysis Methods: Moving averages, trend lines, change point detection, seasonality analysis, baseline comparison
Alert Generation:
- Threshold breaches when metrics exceed limits
- Significant changes (>20% increases/decreases)
- Statistical anomalies in trends
- Unexpected correlations
Example Insights:
- "Gift violations up 45% this month in Sales vs. 6-month average"
- "Conflicts of interest disclosures down 30% in APAC—potential under-reporting"
- "Data privacy incidents cluster in new employee onboarding—training gap"
6. Vector Search Foundation
Why Vector Search Matters
Traditional keyword search is binary—a word appears or doesn't. Vector search understands meaning and context. It knows "accepting gratuities," "receiving gifts," and "taking kickbacks" are conceptually similar despite sharing no words.
Concept: Every document becomes a point in high-dimensional space (384-1,536 dimensions). Documents with similar meanings are geometrically near each other.
Use Cases
- Rule Retrieval for RAG → Most relevant compliance rules for context
- Similar Communication Discovery → "Show all emails similar to this insider trading red flag"
- Historical Case Search → "How did we handle situations like this before?"
- Violation Clustering → Group semantically similar issues
Search Process
Convert query to vector → Calculate distances to indexed vectors → Retrieve k nearest neighbors → Apply metadata filters → Rank by relevance → Fetch full content → Format results
7. Real-Time Monitoring: Alert Broadcasting
The Speed Imperative
In compliance, time is risk. Real-time detection versus weeks-later discovery could mean preventing a regulatory disaster versus suffering one.
Multi-Channel Alerting
Trigger Mechanisms: Threshold-based (risk scores exceed limits), pattern-based (specific violation combinations), trend-based (concerning metric trends), manual escalation
Alert Composition: Severity classification, violation summary, evidence package, risk assessment, recommended actions, historical context, routing information
Distribution Channels:
- Dashboard: Real-time banners, visual indicators, priority inbox
- Email: Detailed reports, targeted stakeholders
- Messaging: Slack/Teams cards with action buttons
- SMS/Phone: Critical alerts, after-hours escalation
- Mobile Push: Native app notifications
Rules Engine: Role-based routing, time-based escalation, acknowledgment tracking, deduplication, aggregation
Live Dashboard Updates
Streaming Architecture: Client opens persistent connection → System monitors database for events → Filter relevant updates → Push to connected clients → Handle disconnects gracefully
Update Types: New alerts, status changes, metric refreshes, analysis completion, system status
8. Building Realistic Test Data
The Quality Paradox
You need data to test but can't use real employee communications (privacy). Intelligent synthetic data generation solves this.
Email Generation Strategy
Template Foundation: Define realistic roles (executives, managers, analysts) → Create scenarios (vendor negotiations, project updates) → Establish conversation patterns → Set metadata distributions
LLM Generation: Provide detailed prompts → Generate natural email content → Inject realistic details → Vary writing styles → Include email artifacts
Violation Injection (15% of corpus):
- Gift acceptance violations (20%)
- Insider trading indicators (15%)
- Conflicts of interest (20%)
- Data privacy breaches (20%)
- Harassment/inappropriate content (10%)
- Financial reporting issues (15%)
Ground Truth Labeling: Binary violation flag, category/type, severity level, specific rule violated, evidence location, expected risk score range
Target Corpus: 3,000 emails (85% compliant, 15% violations) across 6 months, 10 departments, 50 synthetic employees
Transaction Generation
Normal Patterns: Payroll (regular cadence), vendor payments (monthly/quarterly), expense reports (employee-specific), capital expenditures (infrequent, large), revenue transactions
Anomaly Injection (10% of transactions):
- Statistical outliers (3+ standard deviations)
- Temporal anomalies (weekend, after-hours, quarter-end clustering)
- Pattern anomalies (round numbers, just-below-threshold, sequential)
- Relationship anomalies (undisclosed related parties)
9. System Operations
Database Foundation
Core Tables: emails, documents, analysis_results, alerts, themes, transactions, compliance_rules
Reference Tables: users, departments, vendors, rule_categories
Operational Tables: audit_logs, errors, performance_metrics, job_queue
Seed Data: 10 core compliance policies with full text, default configurations, user account templates
Maintenance Operations
Data Lifecycle: Archive data >90 days old, compress archived data, delete temporary data, purge old cache
Database Optimization: Vacuum operations, analyze operations, reindex, partition management
Health Checks: Identify orphaned records, detect inconsistencies, verify integrity
Scheduled: Weekly cleanup, monthly archival, quarterly audits, annual updates
Performance Monitoring
Metrics: Database (connections, query times, locks), Application (throughput, latency, errors), External services (API health), Resources (CPU, memory, disk, network)
Alert Thresholds:
- Critical: Disk >90%, API error >5%, database down
- Warning: Queries >2s, CPU >80%, queue depth >100
10. Security and Audit Trail
Authentication
Methods: Username/password (bcrypt hashing), SSO integration (SAML/OAuth), multi-factor authentication, API keys
Token-Based Sessions: Generate JWT tokens, include user claims, sign cryptographically, short expiration (8 hours) with refresh
Security: Password complexity, account lockout, rate limiting, brute force detection, session invalidation
Authorization
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC):
- Administrator: Full system access
- Compliance Officer: View/act on alerts, run reports
- Analyst: View alerts, limited actions
- Viewer: Read-only dashboards
- Department Head: Own department data only
Enforcement: Check permissions before operations, verify required roles, apply data filtering, log decisions, fail securely (deny by default)
Comprehensive Audit Logging
Logged Events: Authentication, authorization decisions, data access, data modifications, configuration changes, administrative actions, API calls, system events
Log Structure: Timestamp, user ID, session ID, action, resource, IP address, request payload (sanitized), response status, execution duration, metadata
Properties: Immutable, complete, traceable, tamper-evident, retained for regulatory requirements (7 years)
11. Error Handling: Building Resilience
Centralized Error Processing
Classification by Severity: Critical (system down), High (feature unavailable), Medium (performance degradation), Low (handled exceptions)
Classification by Type: Transient (network timeouts), Persistent (configuration errors), External (third-party failures), Internal (bugs)
Handling Process: Capture → Classify → Enrich context → Log → Alert if needed → Recover → Report appropriately
Intelligent Retry Logic
Retry Strategies:
- Exponential Backoff: 5s, 25s, 125s (for rate limits, resource contention)
- Linear Backoff: 30s, 60s, 90s (predictable recovery times)
- Constant Backoff: 60s each (critical operations)
- Jittered Backoff: Add randomness to prevent thundering herd
Circuit Breaker Pattern: Track failure rate → Open circuit after threshold → Periodically test (half-open) → Close when recovered
12. Technology-Agnostic Implementation
Core Patterns Recap
- Master Orchestrator: Single entry point, routing logic, state management, result aggregation
- Multi-Agent Coordination: Specialized agents, state machine workflow, conditional routing, ensemble decisions
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation: Semantic search, grounded responses, vector database, reduced hallucination
- Event-Driven Real-Time: Persistent connections, event streaming, multi-channel alerts
- Synthetic Data Generation: Template-based creation, LLM-powered content, ground truth labeling
Conclusion: The Future of Compliance is Intelligent
The regulatory environment will only grow more complex. Data volumes will only increase. Traditional compliance approaches—sampling, periodic audits, reactive investigations—are becoming obsolete.
This architecture represents a new paradigm: continuous, intelligent, comprehensive compliance monitoring. Through orchestrated AI agents, semantic understanding, real-time alerting, and pattern discovery, organizations achieve the coverage and speed modern regulatory environments demand.
Key Principles
- Orchestration Over Monoliths: Coordinate specialized components
- Intelligence Through Specialization: Multiple focused agents outperform general models
- Grounding Prevents Hallucination: RAG ensures AI operates on facts
- Patterns Over Incidents: Thematic analysis reveals systemic issues
- Real-Time Over Periodic: Immediate detection prevents escalation
- Resilience Through Design: Error handling built into every layer
- Transparency Through Audit: Complete traceability builds trust
These principles apply regardless of technology choices—workflow platforms, traditional frameworks, or cloud-native serverless.
The question is no longer "Can we afford AI-powered compliance monitoring?" but "Can we afford not to?"
The frameworks are proven. The patterns are well-understood. The only variable is implementation commitment. For CFOs and compliance leaders looking to transform from reactive to proactive, from sampling to comprehensive coverage, from lag to real-time—the path forward is clear
Bio
Aryan R. is an MS candidate in Business Analytics & Information Management at Purdue University’s Daniels School of Business. He brings a B.Tech in AI & Data Science and hands-on experience across SQL, Python, visualization, and experimentation. Aryan is passionate about building data-driven products and communicating insights with clarity and precision. Outside academics, he’s a former national-level sprinter who brings the same discipline to his work.
Dr. Rohit Aggarwal is a professor, AI researcher and practitioner. His research focuses on two complementary themes: how AI can augment human decision-making by improving learning, skill development, and productivity, and how humans can augment AI by embedding tacit knowledge and contextual insight to make systems more transparent, explainable, and aligned with human preferences. He has done AI consulting for many startups, SMEs and public listed companies. He has helped many companies integrate AI-based workflow automations across functional units, and developed conversational AI interfaces that enable users to interact with systems through natural dialogue.
You may also like